EM4022V16WS11 데이터 시트보기 (PDF) - EM Microelectronic - MARIN SA
부품명
상세내역
일치하는 목록
EM4022V16WS11
EM4022V16WS11 Datasheet PDF : 15 Pages
| |||
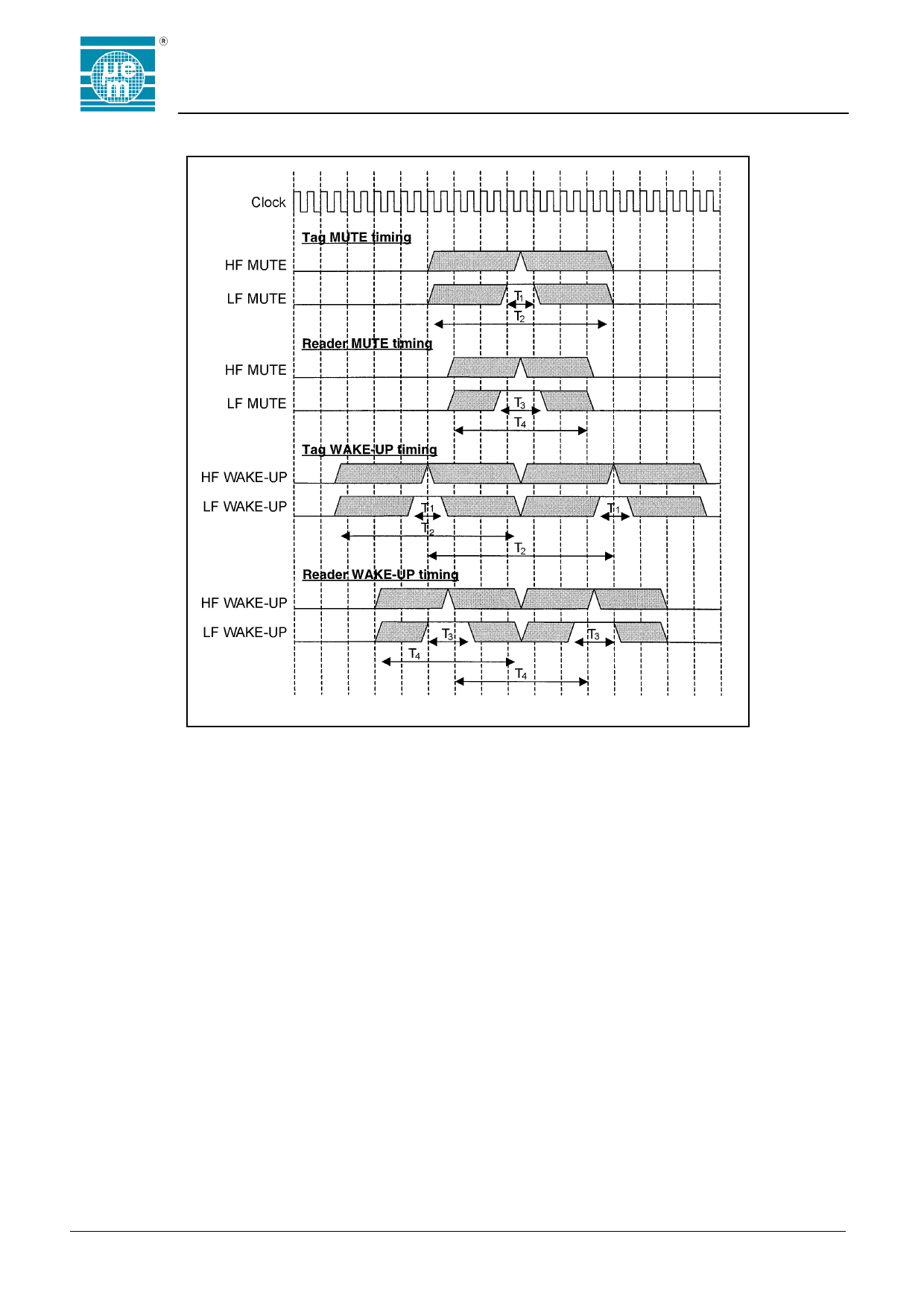
MUTE and WAKE-UP timing diagrams
EM4022
WAKE-UP
An ACK sent after correct reception of a code is
interpreted by the other transponders in the field as a
WAKE-UP. The ACK arrives synchronously at the
transponder that has just transmitted, but
asynchronously at all the other transponders. If
necessary, a WAKE-UP can also be sent if the code is
not received correctly, ensuring that it will not be
interpreted as an ACK by the transmitting transponder.
This could speed up the protocol, but runs the risk of
turning transponders off by accident.
To detect a WAKE-UP, the chip checks for two GAPs,
less than 7 bits apart and each less than seven bits
wide. As with the MUTE allowance must made for the
spread in clock frequencies. To be safely interpreted as
a WAKE-UP, the GAPs should be sent less than 5 bits
apart, and each should be less than 5 bits wide.
Fig. 7
This has an implication in the case of the high frequency
ACK, which could theoretically consist of two very narrow
GAPs 6 bits apart. In practice though, the GAPs will be
typically at least one bit wide, making the separation five
bits.
Like the MUTE, the low frequency ACK GAPs should be
at least 1.5 bits wide to serve as a reliable WAKE-UP.
It should be noted that failure to reliably recognise
WAKE-UPs is not critical. The protocol might be slowed
down marginally, but will still work, as the chips time-out
of the sleep mode automatically after 128 bits.
Copyright 2002, EM Microelectronic-Marin SA
7
www.emmicroelectronic.com